This post is also available in: 

The use of microprocessor chips and industrial electronic equipment and parts in the design of intelligent AC voltage stabilizers (or automatic voltage regulators (AVR)), leads to the production of a high quality and stable power supply, against significant and continuous deviation of the network voltage.
In new generation stabilizers, compared to the previous generation which were of relay type, high performance digital control circuits and SSR is used, and the potentiometer setting is completely removed and allows the user to control the required voltage as well as turning the device on and off through the keyboard.
Table of Contents

Also, this issue accelerates the response time of stabilizers (usually less than a few milliseconds). Today, stabilizers have become a powerful and optimal solution for many electronic devices sensitive to voltage fluctuations and along with many devices such as CNC, air conditioning, television, medical equipment, computer, telecommunication equipment, etc.
What is a voltage stabilizer?
It is an electrical device that sends a constant voltage to the load at its output terminals regardless of the changes in the input voltage.It protects electrical equipment and machines against excessive high or low voltage or other voltage fluctuations.
This device is also called as automatic voltage regulator (AVR).Voltage stabilizers are used for expensive electrical equipment to protect against harmful low/high voltage fluctuations. Some of these equipments are: Air conditioning, offset printing machines, laboratory equipment, industrial machines and medical devices.

Voltage stabilizers regulate input voltage fluctuations before they can damage the load (or equipment sensitive to voltage changes). The output voltage of the stabilizer is set in the range of 230 volts for single-phase systems, and 400 volts for three-phase systems. These adjustments are made by the internal circuit, buck and boost.
There are many types of automatic voltage regulators available in the market. These devices according to the type of application and capacity (KVA) are classified and can be single-phase or three-phase. Three-phase stabilizers are available in two versions, called balanced load models and unbalanced load models.
Stabilizers can be used specifically to stabilize voltage for a single device or to protect a larger unit such as electrical equipment located in a home or office or industrial unit. In addition, they can be analog or digital.

The common types of voltage stabilizers are manually disconnect able and connectable, automatic relay type stabilizers, solid state or static stabilizers and servo motor controlled stabilizers.
In addition to the stabilizer function, most of them have additional features such as input/output low voltage cutoff, input/output high voltage cutoff, overload cutoff, output on and off capabilities, manual/automatic start, voltage cutoff display, and zero voltage switching and so on.
What is the need to use a stabilizer?
In general, any electrical equipment or device is designed for a wide range of input voltage. Depending on the sensitivity, the operating range of the equipment is limited to certain values, for example, some equipment can withstand ±۱۰% of the rated voltage, while others ±۵% or less.
Voltage fluctuations (increase or decrease in nominal voltage value) in many points, especially in connection points to the load is a normal phenomenon. The most common causes of voltage fluctuations are lightning, electrical faults, faulty wiring and periodic shutdown of devices. These fluctuations cause problems for electrical equipment or devices.

Applying excessive overvoltage to the load will bring the following results:
- Permanent damage to equipment
- Damage to the insulation in the coils
- Unwanted interruption in load
- Increased losses in cables and related equipment
- Decreasing the life rating of the device
Applying low voltage to the load will also bring the following results:
- Equipment failure
- Longer working periods (such as resistance heaters)
- Decreasing the proper functioning of the equipment
- larger electrical currents which leads to overheating
- Calculation errors
- Reduce engine speed
Therefore, the stability and accuracy of the voltage determines the correct operation of the equipment. Therefore, voltage stabilizers ensure that voltage fluctuations in the input power supply do not affect the load or electrical device.
How does the voltage stabilizer work? The basis of voltage stabilizer work
to perform Buck and Boost operations
In a voltage stabilizer device, if the input voltage is high, the buck operation is performed and if the input voltage is low, the boost operation is performed until the desired voltage value is reached at the output. This operation can be done manually by switches or automatically through electronic circuits.
The meaning of voltage stabilization is actually adding or reducing the voltage to the input power source. To do such task, the stabilizer uses a transformer that is connected to several relays in different configurations. Some stabilizers use a transformer with taps on the coil to provide various voltage corrections, while servo motor stabilizers use an autotransformer to have a wide range of corrections.
To understand this concept, first consider the 230/12 V step-down transformer and its connection with this operation is given below.
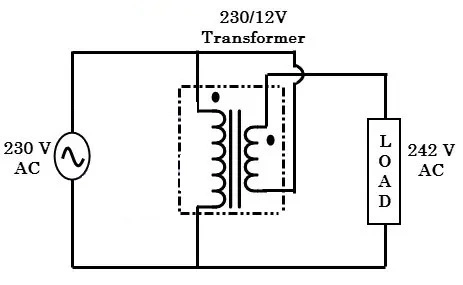
The figure above shows the boosting transformer configuration. where the polarity of the secondary winding is placed in such a way that its voltage is directly added to the primary voltage. Therefore, in under voltage conditions, the transformer (servomotor or autotransformer) is switched by relays or solid state switches to add additional voltages to the input voltage.

The figure above shows the configuration of the step-down transformer (Buck)in which the polarity of the secondary coil is placed in such a way that its voltage is directly reduced from the primary voltage. Therefore, under voltage surge conditions, the transformer (servo motor or autotransformer) is switched by relays or solid state switches to provide additional voltages.

The figure above shows a two-stage voltage stabilizer that consists of two relays to supply Constant ac applied to the load during overvoltage and under voltage. By switching relays, buck and boost operation can be performed for two specific voltage swings (one for low voltage, say 195 V and one for over voltage, say 245 V).
If the stabilizer uses transformer technology with different taps; According to the input voltage, different taps of the transformer enter the circuit. But if the stabilizer has an autotransformer, the servo motor is used to decrease or increase the voltage because the device has only one coil and to increase or decrease the voltage, the servo motor must move in the heads of the transformer coil.
Voltage stabilizers have become an integral part of many household electrical appliances, industries and commercial systems. Previously, manual voltage stabilizers were used to boost or attenuate the input voltage to produce a desired constant output voltage. Such stabilizers used electromechanical relays as a part for disconnecting and connecting.
Later, electronic circuits automated the stabilization process. Another popular type of voltage stabilizers are servo motor stabilizers where voltage correction is done continuously without any key. Let us discuss the three main types of voltage stabilizers.
Types of voltage stabilizers:
In this type of voltage stabilizers, voltage regulation is done by switching relays in such a way that one of a number of taps of the transformer is connected to the load (like the method described above) either for amplification or attenuation operation. The figure below shows the internal circuit of relay type stabilizers.
In the figure, you can see that the device has an electronic circuit and a set of relays next to the transformer. (The transformer can be toroidal or have an iron core with taps located in its secondary part) .Electronic circuit including rectifier circuit, operational amplifier OPAMP, microcontroller unit and other small components.

Voltage stabilizers controlled by servo motor:
The electronic circuit outputs the voltage with the reference value provided by the internal reference voltage source. Whenever the voltage increases or decreases beyond the reference value, the control circuit switches the corresponding relay to connect the desired tap to the output.
These stabilizers usually adjust the output voltage to ±۵ to ±۱۰% for input voltage changes in the range of ±۱۵% to ±۶%. Due to their low weight and low cost, these types of stabilizers are the most used for less important devices in residential, commercial and industrial applications. However, these face several limitations such as low voltage rectification speed, lower durability, lower reliability, power path interruption during regulation, and inability to withstand high voltage fluctuations.
Voltage stabilizers controlled by servo motor:
As the name suggests, it uses a servo motor to enable voltage correction. This category is also known as negative feedback. These are mainly used for high accuracy in output voltage, typically ± ۱% with input voltage variations of up to ± ۵۰%. The figure below shows the internal circuit of a servo stabilizer, which includes the servo motor, auto transformer, buck boost transformer, motor driver and control circuit as necessary components.

In this stabilizer, one primary end of the buck boost transformer is connected to the fixed end of the autotransformer, while the other end is connected to the moving arm controlled by the servo motor. The secondary of the buck boost transformer is connected in series to the input source, which is nothing but the output of the stabilizer.
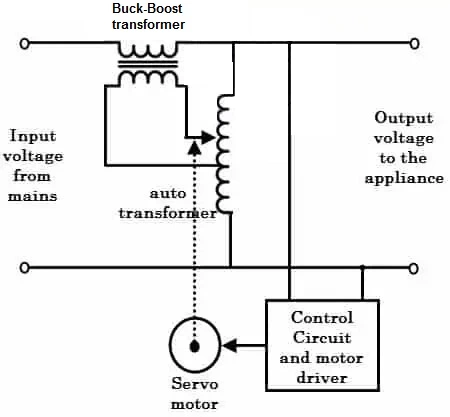
The electronic control circuit detects the amount of voltage drop and voltage increase by comparing the input with an internal reference voltage source. When the circuit detects the fault, it activates the motor which in turn moves the arm of the autotransformer. This can feed the primary buck boost transformer so that a voltage across the secondary should be the desired voltage output.
In the single-phase type, a servo motor can achieve voltage correction through coupling to the autotransformer. In the case of the three-phase balanced type, the servo motor is coupled with three autotransformers to provide a stabilized output during oscillations by adjusting the output of the transformers. In the unbalanced type of servo motor stabilizers, there are three independent servo motors along with three auto transformers and three separate control circuits.

Using servo motor stabilizers has several advantages compared to relay type stabilizers. Some of these are: Higher correction speed, high accuracy of stabilized output, ability to withstand inrush currents and high reliability. However, due to the presence of the motor, these require periodic maintenance.
Static Voltage Stabilizers:
As the name suggests, static voltage stabilizers have no moving parts as a servo motor mechanism. It uses an electronic power converter circuit to achieve voltage regulation as opposed to conventional variac stabilizers. It is possible to produce more accuracy and excellent voltage regulation by these stabilizers compared to servo stabilizers.

These are basically composed of buck boost transformer, IGBT power converter (or AC to AC converter) and microcontroller, microprocessor or DSP based controller. Controlled by a microprocessor, it produces the right amount of voltage with the pulse width modulation technique, and this voltage is supplied to the main buck boost transformer. The IGBT generates the voltage in such a way that it can be in phase or 180 degrees out of phase with the input line voltage to add and subtract the voltages during fluctuations.

Whenever the microprocessor detects a voltage drop, it sends PWM pulses to the IGBT converter to produce a voltage equal to the amount of deviation from the nominal value. This output is in phase with the input source and is applied to the main buck boost transformer. Since the secondary is connected to the input line, the induced voltage is added to the input source and this rectified voltage is applied to the load.
Similarly, an increase in voltage causes the microprocessor circuit to pulse PWM to send it so that the converter is the deviation voltage value with 180 degree phase difference with the input voltage. This voltage is reduced from the input voltage in the secondary of the buck boost transformer to perform the buck operation (voltage reduction).
Compared to servo-motor and relay stabilizers, these stabilizers are very popular due to various advantages such as compact size, very fast correction speed, excellent voltage regulation, maintenance-free due to no moving parts, high efficiency and high reliability.
The difference between stabilizer and AVR voltage regulator:
A major but confusing question arises here, what exactly is the difference(s) between a stabilizer and a regulator? Well. They both do the same job of stabilizing the voltage, but the main difference between a voltage stabilizer and a voltage regulator is:
Voltage Stabilizer: It is a device or circuit that is designed to deliver a constant voltage to the output without changing the input voltage.
Voltage Regulator: It is a device or circuit that is designed to deliver a constant voltage to the output without changing the load current.
How to choose a voltage stabilizer with the right capacity?
Before buying a voltage stabilizer for a device, consider several factors. These factors include: Required wattage of the device, the level of voltage fluctuations experienced at the installation site, device type, stabilizer type, stabilizer working range (correct voltages to which stabilizer), overvoltage/under voltage cut-off, control circuit type, installation type and other factors. Here we have outlined the basic steps you should consider before purchasing a stabilizer for your application.
Determine the specifications of the power consumption of the equipment for which you need to buy a stabilizer from its license plate or from its manual.
Since stabilizers are in kilovolt-amperes (just as transformers are in kilovolt-amperes rather than kilowatts) ,watts can be calculated by multiplying the voltage of the device by the maximum rated current.
It is recommended to add a margin of safety to the stabilizer grade, usually 20-25%. This can be useful for future applications to add more devices to the stabilizer output. .
If the device is rated in watts, consider the power factor when calculating the KVA capacity of the stabilizer.
Below is an example of how to choose the right size voltage stabilizer for your electrical appliances.
Suppose the power of the device (cooler or refrigerator) is 1 KVA. Therefore, a safe margin of 20% is 200 watts. Adding these watts to the actual watts, 1200 VA We receive watts. So the stabilizer is 1.2 kVA or 1200 VA For home needs, 200V to 10kV stabilizers are preferred. And for commercial and industrial applications, single-phase and three-phase large rating stabilizers are used.
It is hoped that the information presented will be informative and useful for the readers. Sincerely ask our dear readers to express their opinions about this article. Thanks to electrical technology!